Nine Hair Loss Mechanisms
Here at Follicular labs we are determined to make products that can tackle everyones hair loss, not just those associated with a single cause. Hair loss can be multi-factored and as a result tackling this hair loss can require mult-factored hair loss solutions.
There are nine major hair loss mechanisms, outlined bellow, and we have formulated our products to tackle several of these major hair loss causes head on with our products.
Hair Loss Mechanisms
[ 1 ] Androgens
Androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a crucial role in hair loss. While androgens stimulate hair in some areas, DHT binds to androgen receptors in scalp follicles, gradually shrinking them and reducing hair growth. This process underlies androgenetic alopecia (AGA), where genetically sensitive follicles miniaturize over time. DHT also disrupts Wnt/β-catenin signaling, essential for follicle maintenance within the anagen phase and further inhibiting regrowth which accelerates hair loss.

Hair Loss Mechanisms
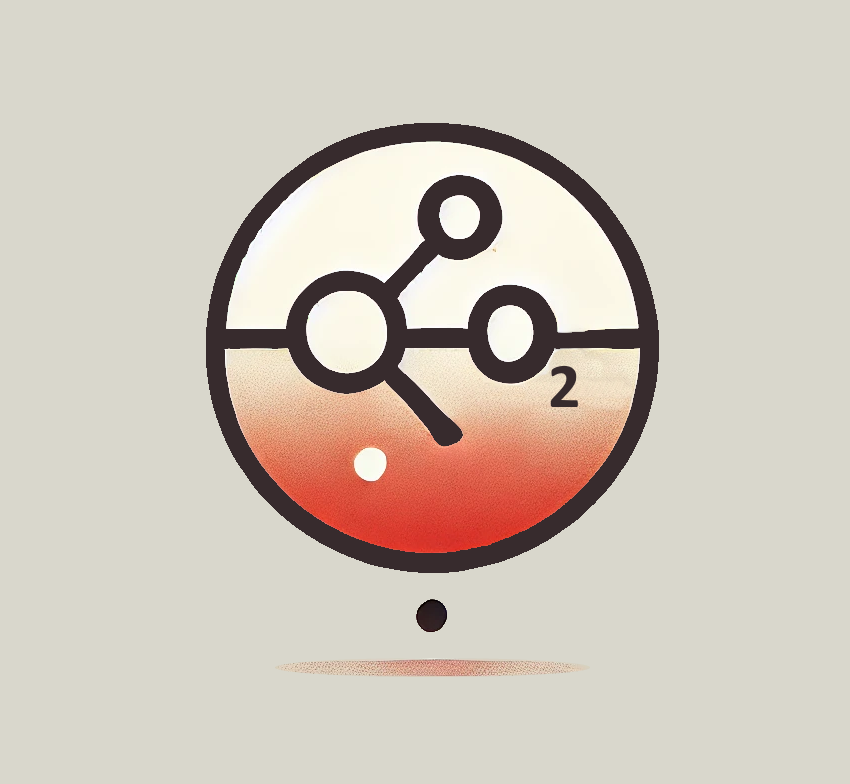
[ 2 ] Oxidation
Oxidation is a chemical process where molecules lose electrons, often due to reactive agents like oxygen, UV light, and pollution. This generates free radicals, unstable compounds that damage lipids, proteins, and DNA, accelerating aging and cellular dysfunction. In hair follicles, oxidative stress can lead to growth arrest or apoptosis, contributing to hair thinning or loss. Antioxidants counteract oxidation by donating electrons, helping to protect hair and skin from damage.

Hair Loss Mechanisms
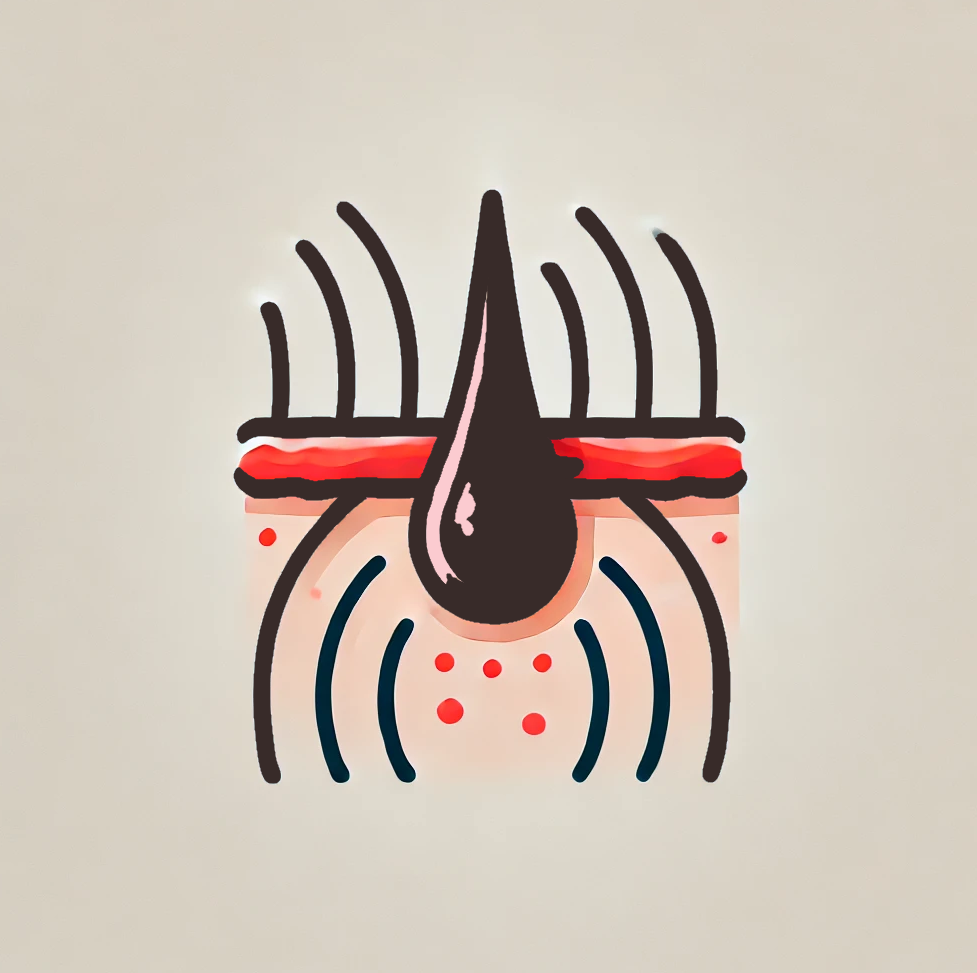
[ 3 ] Inflammation
Inflammation is increasingly recognized as a silent driver of hair loss, even in conditions not traditionally linked to immune response. Low-level, chronic inflammation around hair follicles can disrupt growth cycles, trigger miniaturization, and even cause scarring, often without visible redness. Pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1 and TNF-α damage follicular stem cells, shortening the anagen phase and prolonging telogen, leading to thinner, weaker hair over time.

Hair Loss Mechanisms
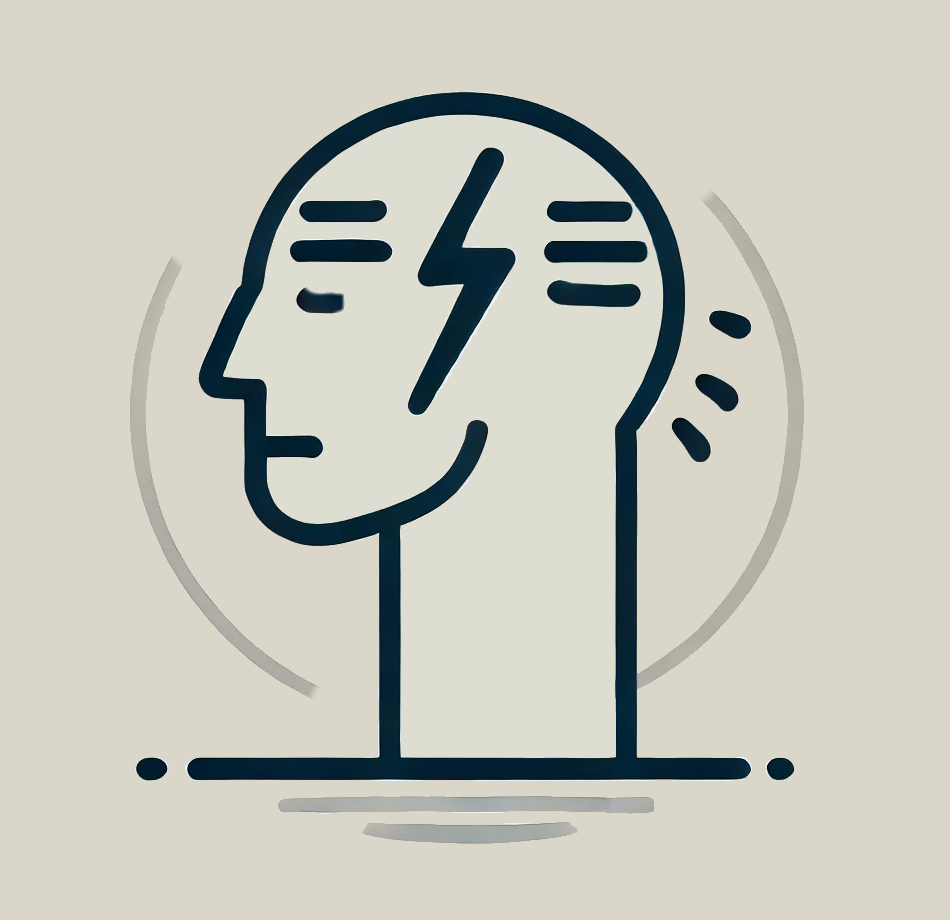
[ 4 ] Stress
Stress is a well-known factor in hair loss, capable of disrupting the hair growth cycle through multiple pathways. Cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, prolongs the telogen (resting) phase, delaying new hair growth. Stress also affects hair follicle stem cells, keeping them dormant and preventing regeneration. Additionally, neuropeptides released during stress trigger inflammation, activating immune cells that release pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6), which impair follicle function. Chronic stress can also overactivate the integrated stress response (ISR), leading to follicular dormancy or cell death. Whether mild or severe, stress accelerates hair shedding by pushing follicles out of anagen (growth) and into telogen, contributing to thinning and loss.
Hair Loss Mechanisms
[ 5 ] Nutrient Deficiencies
Hair follicles rely on a steady supply of proteins, vitamins, and minerals for healthy growth. Deficiencies in protein, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, B-complex vitamins, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Zinc, Iron, and essential fatty acids can lead to thinning, breakage, and disrupted growth cycles. These nutrients support keratin production, follicular cycling, and scalp health, and restoring them through diet, supplements, or topical applications can help promote regrowth and strengthen hair.
Hair Loss Mechanisms
[ 6 ] Blood Flow
Blood flow is vital for hair follicle health, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste. Poor circulation can lead to progressive hypoxic damage, weakening follicles and contributing to hair loss.

Hair Loss Mechanisms
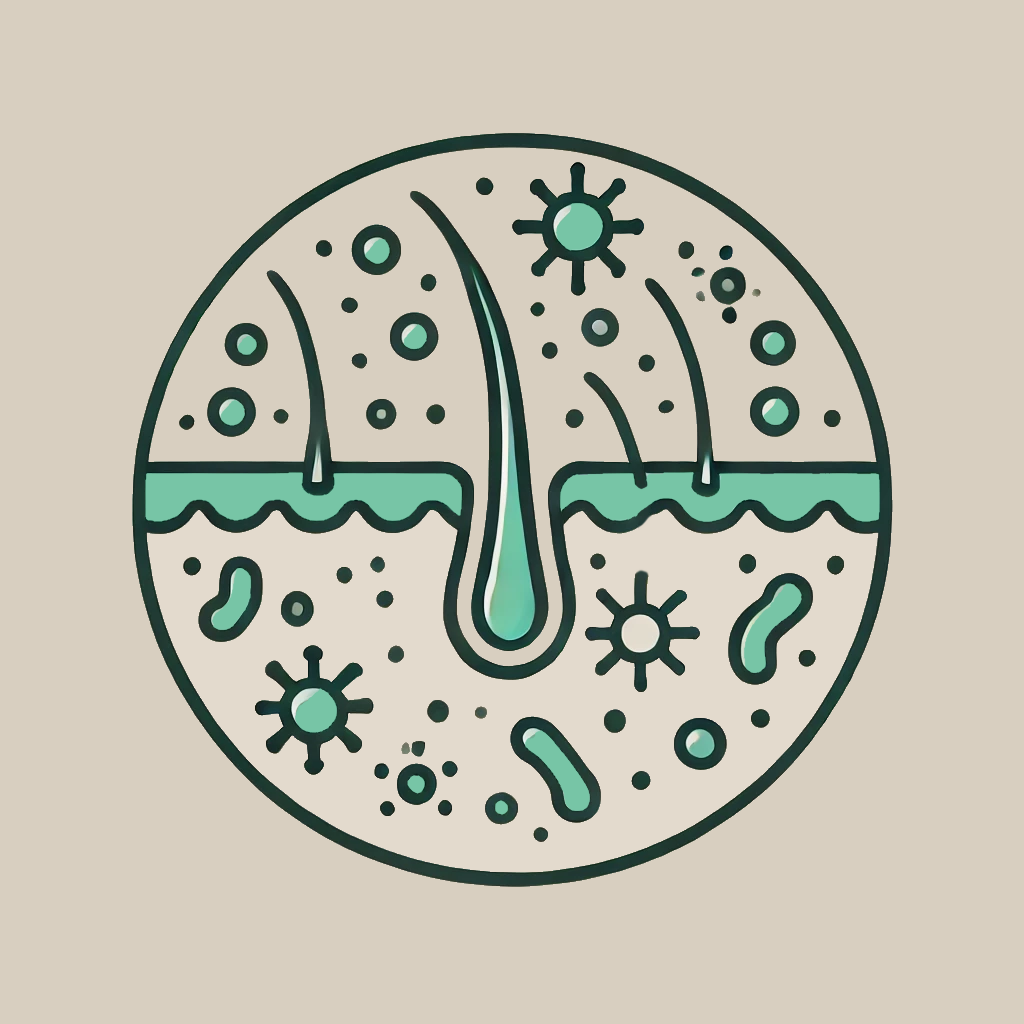
[ 7 ] Microbial Overgrowth
Microbial overgrowth occurs when bacteria or fungi excessively proliferate on the scalp, disrupting the microbiome and contributing to inflammation, follicular damage, and hair loss. Conditions like tinea capitis (fungal infection) and folliculitis (bacterial infection) can weaken hair follicles, while Malassezia overgrowth is linked to dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis which can trigger oxidative stress and inflammation, accelerating shedding. Maintaining a balanced scalp microbiome is essential for healthy hair growth and follicular function.
Hair Loss Mechanisms
[ 8 ] Scalp Dryness
Scalp dryness occurs when the scalp lacks sufficient moisture or there is a compromised skin barrier function which can lead to itching, flaking, and irritation. Factors like cold weather, overwashing, harsh hair products, and skin conditions can strip moisture, weakening the hair. Humectants (e.g., glycerin, hyaluronic acid) draw moisture in, while emollients (e.g., natural oils) lock it in.
Hair Loss Mechanisms
[ 9 ] Reduced Cellular Stimulation
Hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs) growth, dormancy, or senescence are influenced by several factors and biological pathways. Factors like scalp health, nutrition, stress, and hormones impact cellular activity.
Stimulatory pathways (Wnt/β-catenin, SHH, IGF, PDGF, FGF) activate HFSCs, promoting hair regeneration, while inhibitory pathways (TGF-β, BMP, stress hormones) suppress growth. Some pathways (Notch, TLR2) can either stimulate or inhibit depending on context.
Aging and damage push cells into senescence, but managing inhibitory factors and optimizing stimulatory conditions can restore function, supporting hair regrowth and follicular health.
Our Hair Loss Solutions
Below are the active ingredients we use in our Growth Essentials line, including RU58841, GHK-Cu and Vitamin E.
Please click on these to learn more about the supporting research for any of these actives.
Active Ingredients
-
RU58841
RU58841 is a topical androgen receptor antagonist originally researched for prostate cancer but later found to promote hair regrowth by blocking DHT’s effects on follicles. Unlike systemic treatments, it acts locally without significant absorption into the bloodstream. By competitively binding to androgen receptors, RU58841 prevents miniaturization and shedding, making it an effective treatment for the hair loss mechanism [ 1 ] Androgens.
-
GHK-CU (Copper Peptide)
GHK-Cu (Copper peptide) is a naturally occurring peptide bound to copper that promotes hair growth, tissue repair, and anti-inflammatory responses. It reduces oxidative stress, suppresses inflammatory cytokines, supports iron homeostasis, and enhances blood flow through angiogenesis. Additionally, GHK-Cu stimulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling, a key pathway in hair follicle regeneration. This multi-acting molecule combats the hair loss mechanisms [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 5 ], [ 6 ], [ 8 ] and [ 9 ], making it a promising topical treatment for hair regrowth.
-
Vitamin E (D-Alpha Tocopherol Acetate)
Vitamin E (D-α Tocopherol Acetate) is a fat-soluble antioxidant that helps protect hair and scalp health by neutralizing oxidative stress, reducing inflammation, and improving hydration. It prevents lipid peroxidation from UV and pollutants, suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines, and acts as an emollient, enhancing scalp moisture and barrier function. Well-tolerated topically, Vitamin E counters the hair loss mechanisms, [ 2 ], [ 3 ] and [ 8 ].